What Are Hemorrhoids?
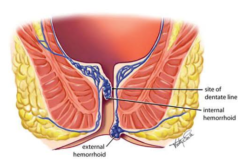
Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the rectum or anus caused by increased pressure in these areas. They are common and can occur in both men and women, often as a result of straining during bowel movements, prolonged sitting, or pregnancy. Hemorrhoids are classified into two main types: internal and external.
Internal hemorrhoids form inside the rectum and are usually painless, but they may bleed during bowel movements. External hemorrhoids develop under the skin around the anus, leading to discomfort, swelling, and itching. While mild hemorrhoids can often be treated at home, severe cases may require medical intervention, including surgery.
Symptoms of Hemorrhoids
The symptoms of hemorrhoids can vary depending on their type and severity. Common signs include:
- Pain or discomfort, particularly during bowel movements. This is more common with external hemorrhoids or prolapsed internal hemorrhoids.
- External hemorrhoids often cause itching or irritation around the anus.
- Bleeding during bowel movements typically appears as bright red blood on toilet paper or in the toilet bowl.
- Swelling or a lump near the anus. This is a common symptom of external hemorrhoids and may cause tenderness or pain.
- Prolapse, where an internal hemorrhoid extends outside the anus. Prolapsed hemorrhoids may cause discomfort and require manual retraction or medical attention.
While occasional discomfort may resolve with home treatments, a healthcare provider should evaluate persistent or severe symptoms.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Hemorrhoids can often be managed with over-the-counter treatments and lifestyle changes. Still, certain signs indicate the need for professional care. If you experience heavy bleeding, severe pain, or swelling that does not improve with home remedies, you should consult a doctor. Symptoms like frequent bleeding or changes in bowel habits may also point to other conditions, such as colorectal cancer, and should be checked promptly.
Suppose hemorrhoids prolapse and cannot be pushed back inside or become thrombosed (develop a blood clot). In that case, immediate medical attention may be necessary. Chronic hemorrhoids that interfere with daily life or fail to respond to non-surgical treatments may require surgical intervention.
Surgical Options for Hemorrhoids
When hemorrhoids are severe or persistent, surgery may be recommended. Several effective procedures can provide long-term relief:
Rubber Band Ligation
This minimally invasive procedure is commonly used for internal hemorrhoids. A small rubber band is placed around the base of the hemorrhoid, cutting off its blood supply. The hemorrhoid shrinks and falls off within a few days. Rubber band ligation is typically quick and does not require anesthesia. Still, mild discomfort may occur for a few days after the procedure.
Sclerotherapy
Sclerotherapy involves injecting a chemical solution into the hemorrhoid, causing it to shrink. This procedure is often used for smaller hemorrhoids or those that bleed frequently. It is relatively painless and can be performed in a doctor’s office.
Hemorrhoidectomy
Hemorrhoidectomy is a surgical procedure to remove large or severe hemorrhoids. It is typically recommended for cases where other treatments have failed or when hemorrhoids are causing significant discomfort. The surgeon removes the swollen tissue during the procedure, providing permanent relief. Recovery from a hemorrhoidectomy can take a few weeks, and patients may experience some pain during healing, but the results are highly effective.
Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy
This procedure is often used for prolapsed internal hemorrhoids. A stapling device is used to reposition the hemorrhoid back inside the rectum and cut off its blood supply. Stapled hemorrhoidopexy generally has a shorter recovery time than a traditional hemorrhoidectomy. Still, it may not be suitable for external hemorrhoids.
Recovery After Hemorrhoid Surgery
Recovery times vary depending on the type of surgery performed. Minimally invasive procedures like rubber band ligation and sclerotherapy typically allow patients to return to normal activities within a day or two. More invasive surgeries, such as hemorrhoidectomy, may require a longer recovery period.
During recovery, following your doctor’s instructions is important to minimize discomfort and prevent complications. Sitz baths, where you soak the anal area in warm water for 15-20 minutes, can help reduce pain and swelling. Staying hydrated and eating a high-fiber diet can prevent constipation and reduce the risk of straining during bowel movements, which is crucial for proper healing.
During the recovery period, avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activities. If pain persists or symptoms worsen, contact your healthcare provider for follow-up care.
Conclusion: Effective Treatment for Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids are a common condition that can cause discomfort and irritation, but they are treatable. Recognizing and addressing the symptoms early with home remedies or non-surgical treatments can often provide relief. For chronic or severe hemorrhoids, surgical options such as rubber band ligation, sclerotherapy, or hemorrhoidectomy offer effective solutions.
If you experience persistent symptoms or significant discomfort, consult a doctor to determine the best treatment plan. With the right care, you can find relief and prevent future problems.
