Introduction: The Intersection of Pregnancy and Hemorrhoids
Pregnancy is a time of profound change, both emotionally and physically. As the body adapts to support a growing baby, many women experience various new health challenges. One common issue is the development of hemorrhoids—swollen, inflamed veins in the rectal area that can cause discomfort and pain. Although hemorrhoids are not exclusive to pregnancy, the physiological changes that occur during this period make women more susceptible to developing them. Understanding why hemorrhoids arise during pregnancy is crucial for early intervention, prevention, and effective management, ultimately ensuring a healthier and more comfortable pregnancy journey.
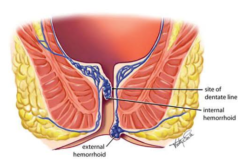
What Are Hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids are essentially enlarged veins located in the lower rectum and anus. They can be internal, forming inside the rectum, or external, appearing under the skin around the anus. While internal hemorrhoids may be painless, they can lead to bleeding. In contrast, external hemorrhoids are often associated with significant pain, especially if they become thrombosed. For many, these swollen veins are a temporary inconvenience; however, during pregnancy, they can add to the discomfort already experienced due to other pregnancy-related changes.
How Pregnancy Contributes to Hemorrhoids
During pregnancy, the body undergoes several changes that create an environment in which hemorrhoids are more likely to develop. One of the primary reasons is the increased blood volume and pressure exerted on the pelvic veins. As the uterus grows, it presses against the surrounding blood vessels, including those in the rectal area, which can cause them to swell. Hormonal fluctuations, particularly the rise in progesterone levels, also play a significant role. Progesterone relaxes the smooth muscles throughout the body, including the walls of blood vessels, which can weaken the vein walls and contribute to the formation of hemorrhoids.
Another contributing factor is constipation, a common complaint during pregnancy. Changes in diet, reduced physical activity, and the effects of progesterone can slow down the digestive process, making bowel movements infrequent and more challenging to pass. Straining during bowel movements increases pressure on the anal veins, further exacerbating the risk of developing hemorrhoids. For more detailed insights into hemorrhoids during pregnancy, you can visit Mayo Clinic’s Hemorrhoids Overview.
Understanding the Causes: Physiological and Lifestyle Factors
Several key factors contribute to the development of hemorrhoids during pregnancy:
Firstly, the physical pressure exerted by the expanding uterus is a major contributor. As the baby grows, the uterus occupies more space and presses against the pelvic veins. This pressure hinders proper blood flow and causes the veins in the rectal area to dilate. Secondly, hormonal changes—particularly the increase in progesterone—relax the blood vessel walls, making them more prone to swelling under pressure. This dual effect of increased pressure and relaxed veins creates the perfect conditions for hemorrhoids to form.
Dietary habits during pregnancy also play a significant role. Many women experience changes in their appetite and food preferences during pregnancy, and sometimes, these changes lead to a diet that is low in fiber. A low-fiber diet can contribute to constipation, which, as mentioned earlier, is a significant risk factor for hemorrhoids. Inadequate fluid intake may compound the problem, as hydration is crucial for maintaining soft, easily passable stools.
Moreover, lifestyle factors such as reduced physical activity during pregnancy can further impair digestion. While many expectant mothers are encouraged to stay active, discomfort and fatigue may lead to a more sedentary lifestyle, exacerbating constipation and increasing the strain during bowel movements. Stress, which can be high during pregnancy due to emotional and physical changes, may also indirectly affect bowel function, further increasing the risk of hemorrhoid development.
Prevention Strategies: Proactive Measures During Pregnancy
Prevention is always preferable to treatment. Pregnant women can adopt several strategies to reduce the risk of developing hemorrhoids:
Focusing on a high-fiber diet is one of the most effective preventive measures. Incorporating a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes into daily meals helps promote regular bowel movements and prevents constipation. Staying well-hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day is also essential. Regular physical activity, even gentle exercise like walking or prenatal yoga, can stimulate digestion and improve overall circulation, reducing the pressure on pelvic veins.
Another crucial preventive strategy is to avoid straining during bowel movements. Establishing regular bathroom habits and responding promptly to the natural urge to defecate can help minimize the pressure on the anal region. Pregnant women may also find relief by taking warm sitz baths, which can soothe the affected area and reduce discomfort. Additionally, using topical treatments, such as over-the-counter creams or suppositories specifically designed for hemorrhoid relief, can provide temporary symptom relief.
Managing Hemorrhoids if They Develop
Despite taking preventive measures, some women may still develop hemorrhoids during pregnancy. Early management is key to reducing discomfort and preventing further complications when this occurs. Conservative treatment methods include lifestyle and dietary modifications, as well as the use of topical medications. Ensuring that constipation is managed effectively through increased fiber and fluid intake is essential. When approved by a healthcare provider, mild over-the-counter pain relievers can help alleviate discomfort.
In cases where hemorrhoids become particularly painful or do not improve with conservative measures, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider. Although surgical intervention is generally avoided during pregnancy unless necessary, there are minimally invasive procedures that can be considered postpartum if hemorrhoids persist and cause significant distress.
Long-Term Considerations: Postpartum and Beyond
For many women, hemorrhoids that develop during pregnancy resolve after childbirth as the pressure on the pelvic veins decreases and hormonal levels return to normal. However, some women may continue to experience symptoms postpartum. Maintaining a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and proper hydration remain essential even after delivery to promote overall digestive health and prevent recurrence.
Follow-up with a healthcare provider can help monitor the condition and address any lingering symptoms. It is also beneficial to discuss long-term strategies for maintaining bowel health, mainly if there is a history of hemorrhoids during pregnancy. Continued education about nutrition and lifestyle adjustments can empower women to manage their digestive health proactively.
Psychological and Emotional Impact
The experience of dealing with hemorrhoids during pregnancy can be stressful and may affect emotional well-being. The discomfort and potential embarrassment associated with hemorrhoids, coupled with the overall stress of pregnancy, can take a toll on mental health. Expectant mothers need to seek support from healthcare providers, family, or support groups to help manage both the physical and emotional challenges. Open communication about these issues can lead to better management strategies and reassurance during significant change.
Conclusion: Empowering Your Pregnancy Journey
Hemorrhoids during pregnancy are a common issue that arises from the physiological and hormonal changes inherent to this special time. Increased pressure on pelvic veins, hormonal fluctuations, and dietary challenges combine to create an environment where hemorrhoids can develop. By understanding these causes, you can take proactive steps to prevent or manage this condition, ensuring a more comfortable pregnancy experience.
Adopting a high-fiber diet, staying hydrated, engaging in regular physical activity, and avoiding straining during bowel movements are key preventive measures. If hemorrhoids do develop, early management through lifestyle adjustments and conservative treatments can alleviate discomfort and prevent complications. Remember, postpartum recovery often brings relief as the body gradually returns to its pre-pregnancy state, though maintaining healthy habits remains essential.
Empower yourself with knowledge and proactive care to navigate the challenges of hemorrhoids during pregnancy. Regular communication with your healthcare provider and a commitment to a healthy lifestyle can make all the difference in your overall well-being. Embrace the journey, knowing that small, consistent steps toward prevention and management will help ensure a healthier, more comfortable pregnancy and beyond.
