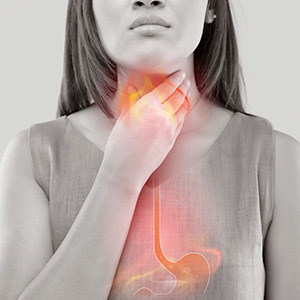
GERD, or Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, is a chronic condition where stomach acid frequently flows back into the tube connecting the mouth and stomach, causing irritation. This tube, known as the esophagus, is not equipped to handle such acidic substances and can lead to a range of symptoms. GERD is a common digestive disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is estimated that around 20% of adults in the United States suffer from GERD at least once a week.
Diving Deep into the Primary Causes of GERD
GERD results from a weakened lower esophageal sphincter, allowing stomach acid to reflux into the esophagus. Factors like obesity, diet, and certain medications can contribute. However, GERD can also be caused by anatomical abnormalities such as a hiatal hernia or pregnancy. One of the main causes is poor eating habits, including consuming large meals and lying down after eating. This can increase pressure on the lower esophageal sphincter, making it easier for stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus.
Lifestyle Factors: Their Contribution to GERD Development
Smoking, excessive caffeine intake, and alcohol consumption are known triggers. Moreover, lying down immediately after meals can exacerbate reflux episodes. Stress is also believed to play a role in GERD development, as it can increase acid production and cause muscles in the esophagus to relax. Poor sleeping habits, such as sleeping on an incline or too many pillows, may also contribute to GERD symptoms.
Medical Conditions and Medications: Uncovering Lesser-Known Causes of GERD
Conditions like hiatal hernia, pregnancy, and connective tissue disorders increase GERD risk. Medications such as antihistamines, calcium channel blockers, and painkillers can also contribute. Additionally, certain medical conditions like asthma, diabetes, and scleroderma have been linked to GERD development. It is important to discuss any existing medical conditions and medications with a healthcare provider, as they may be contributing factors to GERD.
Diet and GERD: Foods that Trigger and Alleviate Symptoms
Foods like citrus fruits, spicy foods, and caffeinated drinks can trigger GERD. On the contrary, foods like ginger, oatmeal, and lean meats might help alleviate symptoms. Keeping a food diary and tracking symptoms can help identify specific triggers. It is also recommended to eat smaller meals throughout the day and avoid eating close to bedtime.
Preventing GERD: Effective Strategies for Long-term Relief
Prevention starts with understanding and avoiding personal triggers. Regular, smaller meals and raising the head of the bed can also help. Avoiding tight-fitting clothing, quitting smoking, and managing stress can also reduce GERD symptoms. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to strengthen the lower esophageal sphincter and prevent acid reflux.
Understanding the Role of Weight Management in Preventing GERD
Excess weight, especially around the abdomen, can increase pressure on the stomach, causing reflux. Maintaining a healthy weight can significantly reduce GERD episodes. Exercise can also help strengthen the muscles at the bottom of the esophagus and improve digestion.
Effective Eating Habits to Reduce GERD Occurrences
Eating slowly, avoiding late-night meals, and ensuring not to lie down for at least 3 hours post meals can reduce reflux chances. Additionally, consuming smaller meals and snacking on healthy options can also help prevent GERD symptoms. It is also advised to stay well-hydrated throughout the day.
Beyond Diet: Holistic Lifestyle Changes to Ward Off GERD
Managing stress, refraining from tight-fitting clothes, and adopting an active lifestyle can holistically reduce GERD risk and promote overall digestive health. Additionally, avoiding tobacco and limiting alcohol intake can also help prevent GERD symptoms.
Conclusion: Taking Control of GERD with a Comprehensive Approach
Overall, GERD is a common condition that can significantly impact one's quality of life. While medication can provide relief, taking a comprehensive approach by addressing lifestyle factors and incorporating dietary changes can greatly reduce the occurrence of reflux episodes and promote long-term relief. By understanding the primary causes and triggers of GERD, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their symptoms and prevent future occurrences. It is essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plans. With the right approach, individuals can effectively take control of GERD and improve their overall well-being. So, if you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of GERD, don't hesitate to seek medical advice and make the necessary lifestyle changes for long-term relief. Remember, prevention is key to managing GERD and promoting a healthy digestive system. So start making those dietary and lifestyle adjustments today!
