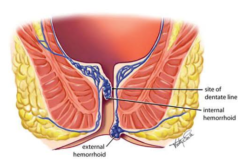
Hemorrhoids, often known as piles, are swollen veins located in the lowest part of the rectum and anus, similar to varicose veins. While they are a common condition, not all cases require surgery. Understanding the symptoms of hemorrhoids can help determine when medical attention or surgical intervention might be necessary.
Symptoms of Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids can present with a variety of symptoms, depending on whether they are internal or external:
- Bleeding during bowel movements: One of the most common signs of hemorrhoids is noticing specks of bright red blood on toilet paper or in the toilet bowl.
- Pain and discomfort: External hemorrhoids, and sometimes prolapsed internal hemorrhoids, can cause pain, especially during or after bowel movements.
- Itching or irritation: The area around your anus may feel itchy or irritated due to external hemorrhoids.
- Swelling around the anus: This is more commonly associated with external hemorrhoids.
- A lump near your anus: You may feel or see a lump, which could be painful, near your anus. This is characteristic of external hemorrhoids or prolapsed internal hemorrhoids.
- Leakage of feces: Hemorrhoids can cause an inability to control bowel movements, leading to fecal leakage.
When Is Surgery Necessary?
Most hemorrhoid symptoms can be managed with lifestyle changes, over-the-counter (OTC) treatments, and home remedies. However, surgery might be considered in the following scenarios:
- Persistent symptoms: If symptoms remain severe and persistent despite conservative treatments, such as dietary changes, OTC medications, and sitz baths.
- Large hemorrhoids: Large external or prolapsed internal hemorrhoids may not respond well to non-surgical treatments and can be effectively treated with surgical intervention.
- Complications: If complications arise, such as significant bleeding, thrombosis (clotting), or anemia from chronic blood loss, surgery may be required to resolve these issues.
Surgical Options for Hemorrhoids
Several surgical procedures are available for treating hemorrhoids, including:
- Hemorrhoidectomy: This procedure involves the removal of excessive tissue causing bleeding or discomfort. It's considered the most effective method for severe or recurrent hemorrhoids but comes with a longer recovery period.
- Rubber Band Ligation: A rubber band is placed around the base of the hemorrhoid inside the rectum, cutting off its blood supply and causing it to wither and fall off. It's a common treatment for internal hemorrhoids.
- Sclerotherapy: A chemical solution is injected into the hemorrhoid tissue, causing it to shrink. This is typically used for smaller hemorrhoids.
- Infrared Coagulation: A device is used to apply infrared light to the hemorrhoidal tissue, causing it to form scar tissue and cut off blood supply to the hemorrhoid.
Post-Surgical Care and Recovery
Post-surgical care and recovery play a crucial role in ensuring a smooth healing process after hemorrhoid surgery. Patients are typically advised to follow a fiber-rich diet to soften stools and prevent straining during bowel movements, which is essential in avoiding recurrence. Managing pain with prescribed or over-the-counter pain relievers, and maintaining personal hygiene with gentle cleaning methods, can also help in reducing discomfort and preventing infection. Additionally, regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider are important to monitor healing progress and to address any concerns that may arise post-surgery.
Lifestyle Changes and Preventative Measures
To minimize the risk of hemorrhoids or prevent their recurrence after treatment, adopting lifestyle changes is crucial. Simple modifications such as incorporating a diet rich in fiber from fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can significantly improve bowel health. Increased water intake is equally important, as it helps soften stool, making bowel movements less straining. Regular exercise promotes digestive health and reduces the pressure on veins in your lower rectum and anus caused by prolonged sitting or standing. Lastly, avoiding delaying bowel movements can help prevent the stool from becoming hard and difficult to pass, thus reducing the strain on rectal and anal veins.
Conclusion
Hemorrhoids are a prevalent condition with a variety of treatments available, ranging from lifestyle adjustments to surgical interventions. Surgery is generally reserved for severe cases or when other treatments have failed to alleviate symptoms. If you experience symptoms of hemorrhoids that impact your quality of life or suspect you may need surgical treatment, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. Early intervention can prevent complications and lead to a better outcome.
