What is colon cancer?
Colon cancer is a type of colorectal cancer which occurs in either the colon or rectum. Colorectal cancers are among the most common and deadliest forms of cancer in humans. It is also known as bowel cancer since it affects the large intestine (colon) and/or rectum. The first symptom of colorectal cancer can be blood on your stool or black stools that look like tar, but this may not occur until colorectal cancer has spread to other organs such as your liver or lungs.
What are the symptoms of colon cancer?
The symptoms listed above are usually found only at the late stages of colorectal cancers. For example, if you have been constipated for more than three weeks without any other explanation, then you should see your doctor.
Colorectal cancer is preventable if it is caught early. Colorectal cancer screening such as colonoscopy can find polyps (abnormal growths on the lining of the intestine) before they turn into cancer. If you have a family history of colorectal cancer, then you should start getting screened at a younger age.
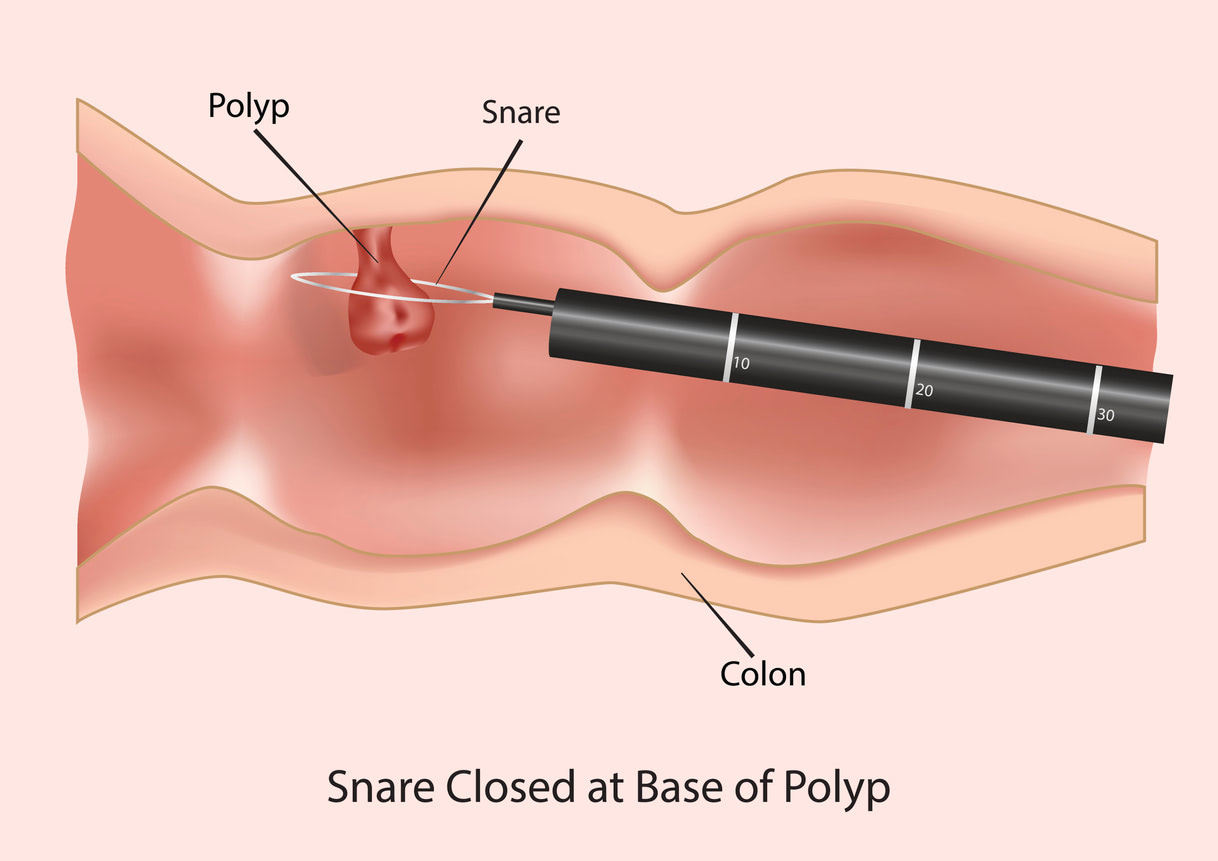
What is a colonoscopy?
A colonoscopy is an examination of the large intestine using a long, thin tube with a camera lens at one end. The camera sends pictures to a computer screen, so your doctor can see if you have any polyps or other abnormalities. If polyps are found, they can be removed during the same procedure.
Most people do not have any problems after a colonoscopy. However, you may have some minor cramping or bloating. If you do have any problems, they usually go away within a few days.
You should get a colorectal cancer screening if you are over the age of 50, have a family history of colorectal cancer, or have other risk factors such as obesity or diabetes. Talk to your doctor about which colorectal cancer screening test is right for you.
Screening tests such as colonoscopy can find polyps before they turn into cancer. If you have a family history of colorectal cancer, then you should start getting screened at a younger age.
A colonoscopy is an examination of the large intestine using a long, thin tube with a camera lens at one end. The camera sends pictures to a computer screen, so your doctor can see if you have any polyps or other abnormalities. If polyps are found, they can be removed during the same procedure.
Most people do not have any problems after a colonoscopy. However, you may have some minor cramping or bloating. If you do have any problems, they usually go away within a few days.
colorectal cancer risk factors:
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Smoking
- Heavy alcohol use
- A family history of colorectal cancer.
Colorectal cancer is preventable if it is caught early. Colorectal cancer screening such as colonoscopy can find polyps (abnormal growths on the lining of the intestine) before they turn into cancer. If you have a family history of colorectal cancer, then you should start getting screened at a younger age.
Colon cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths in America. Colonoscopies are a potentially life-saving procedure for colorectal cancers and other health problems that can be diagnosed during colonoscopies, such as polyps or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
The screening process involves inserting a flexible tube with an attached camera into your rectum to examine the lining of your large intestine. This test should be performed at least every ten years if you're 50 years old or older, especially because colorectal cancers typically have no symptoms until they've grown quite advanced.
If you don't know whether it's time for you to get screened yet, ask yourself these questions: Do I experience any unexplained weight loss? Diarrhea that lasts more than a week? These are all symptoms of colorectal cancer, and it's important to address them as soon as possible. If so, then you should go see a doctor.
