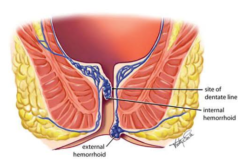
Internal hemorrhoids are swollen blood vessels that form inside the rectum. Unlike external hemorrhoids, which are located under the skin around the anus, internal hemorrhoids are typically not visible and are usually less painful. However, they can cause discomfort and other noticeable symptoms, particularly when they strain, bleed, or protrude (prolapse) through the anus. Understanding the symptoms and available treatments is essential for managing this condition effectively.
Symptoms of Internal Hemorrhoids
Internal hemorrhoids are classified into four grades based on their severity and symptoms:
- Grade I: Hemorrhoids that bleed but do not prolapse.
- Grade II: Hemorrhoids that prolapse and retract on their own during a bowel movement.
- Grade III: Hemorrhoids that prolapse and require manual repositioning.
- Grade IV: Hemorrhoids that are prolapsed and cannot be manually repositioned.
The most common symptom of internal hemorrhoids is painless bleeding during bowel movements. You might notice small amounts of bright red blood on your toilet tissue or bowl. Other symptoms can include itching, rectal discomfort, and a feeling of fullness or discomfort in the rectum. Prolapsed hemorrhoids may produce a sensation of moisture or the feeling of a lump protruding from the anus.
Treatment Options for Internal Hemorrhoids
The treatment for internal hemorrhoids varies depending on the severity of the symptoms and the grade of the hemorrhoid. Options include:
- Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies: For mild symptoms, increasing fiber intake through diet or supplements can help reduce constipation and straining during bowel movements, thereby alleviating symptoms. Staying hydrated, practicing good hygiene, and taking warm sitz baths can also provide relief.
- Medications: Over-the-counter (OTC) topical treatments, such as creams, ointments, or suppositories, may offer temporary relief from mild discomfort and itching, although they don't cure hemorrhoids.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: For more persistent or severe hemorrhoids, doctors may recommend office-based procedures, including:
- Rubber Band Ligation: Small rubber bands are placed around the base of the hemorrhoid to cut off its blood supply, causing it to wither and fall off.
- Sclerotherapy: A chemical solution is injected into the hemorrhoid tissue to shrink it.
- Infrared Coagulation: Infrared light is used to heat and scar the hemorrhoid tissue, reducing blood flow to the hemorrhoids.
- Surgery: In cases of large, persistent, or severely prolapsed hemorrhoids, surgical intervention may be necessary. Procedures like hemorrhoidectomy (removal of the hemorrhoid) or hemorrhoidopexy (stapling of the hemorrhoid) are performed in a hospital under anesthesia and are typically reserved for the most severe cases.
Preventing Internal Hemorrhoids
Prevention of internal hemorrhoids centers around mitigating the risk factors associated with their development. This includes adopting a diet high in fiber from fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to ensure soft stools and minimize straining during bowel movements. Regular physical activity is also recommended to prevent constipation, a significant contributing factor. Additionally, avoiding prolonged sitting and ensuring timely bowel movements without straining can help reduce the pressure on the veins in the lower rectum, further decreasing the likelihood of hemorrhoid development.
Lifestyle Modifications for Enhancing Treatment Outcomes
Incorporating simple lifestyle modifications is instrumental in enhancing treatment outcomes for individuals suffering from internal hemorrhoids. Prioritizing hydration by drinking ample water throughout the day softens the stool, making bowel movements less strenuous and reducing the risk of hemorrhoid exacerbation. Additionally, engaging in regular, moderate exercise helps maintain bowel regularity and reduces pressure on veins in the lower rectum caused by prolonged sitting or standing. Lastly, establishing a consistent routine for bowel movements without forcing or delaying the natural urge can significantly contribute to mitigating symptoms and preventing further hemorrhoid development.
Conclusion
Internal hemorrhoids, while less painful than their external counterparts, can cause significant discomfort and impact quality of life. Fortunately, a range of treatments, from simple dietary adjustments to surgical interventions, is available to manage symptoms effectively. If you suspect you have internal hemorrhoids, particularly if you experience rectal bleeding, it's important to seek a medical evaluation to confirm the diagnosis and discuss the most appropriate treatment options for your specific situation. With the right approach, most people can achieve significant relief from hemorrhoid symptoms.
