Introduction: Understanding Internal Hemorrhoids
Internal hemorrhoids are swollen veins located inside the rectum that often go unnoticed until symptoms develop. Unlike their external counterparts, internal hemorrhoids are typically painless; however, they can cause significant discomfort when complications occur. During periods of straining or irritation, these hemorrhoids may bleed or protrude from the anus, leading to symptoms that interfere with daily activities and overall well-being. Effective treatment and proper management of symptoms are essential to alleviate discomfort and prevent further complications. This article provides an in-depth look at internal hemorrhoids, their symptoms, and various treatment options.
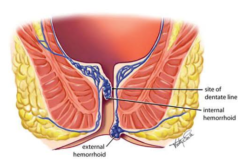
What Are Internal Hemorrhoids?
Internal hemorrhoids form within the lining of the rectum and are usually covered by a mucous membrane, making them less visible and often less painful than external hemorrhoids. They develop as a result of increased pressure in the rectal veins, which can be caused by several factors, including chronic constipation, prolonged sitting, pregnancy, or straining during bowel movements. Although many individuals may have internal hemorrhoids without experiencing any symptoms, issues arise when these veins become inflamed or damaged.
The progression of internal hemorrhoids can vary. In some cases, they remain small and asymptomatic. In contrast, in others, they may enlarge and prolapse, meaning they protrude from the anus during bowel movements. When this happens, symptoms such as bleeding and discomfort become more pronounced, necessitating medical attention and proper management strategies.
Recognizing the Symptoms
While internal hemorrhoids often do not cause pain due to the lack of nerve endings in the affected area, several symptoms may still alert you to their presence. The most common symptoms include:
- Painless Bleeding: Bright red blood may appear on the toilet paper or in the toilet bowl after a bowel movement. This is one of the hallmark signs of internal hemorrhoids.
- Mucus Discharge: Some individuals notice mucus coming from the anus, which can be associated with internal hemorrhoids.
- A Feeling of Incomplete Evacuation: Patients may feel as though they have not completely emptied their bowels, which can be uncomfortable and distressing.
- Prolapse: In more advanced cases, internal hemorrhoids can protrude through the anal opening during bowel movements. This can lead to discomfort, especially if the prolapsed tissue becomes irritated or trapped outside the anus.
- Itching or Irritation: Although less common than with external hemorrhoids, some individuals may experience mild itching or irritation around the anal area if the hemorrhoids become aggravated.
Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial, as it allows prompt treatment and helps prevent the condition from worsening.
Treatment Options for Internal Hemorrhoids
Managing internal hemorrhoids effectively involves a combination of non-surgical and, in some cases, surgical interventions. The treatment choice depends on the severity of the symptoms and the overall impact on your quality of life.
Conservative Treatments
For many individuals, internal hemorrhoids can be managed with non-surgical approaches that aim to reduce inflammation, ease symptoms, and prevent complications.
Dietary Modifications and Lifestyle Changes:
A high-fiber diet is one of the most effective ways to manage hemorrhoids. Consuming plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes can help soften stools and promote regular bowel movements, reducing the need to strain. Drinking plenty of water is essential, as hydration is key to maintaining smooth digestive function. Regular physical activity also helps improve bowel motility and reduces the pressure on the rectal veins.
Over-the-Counter Remedies:
Various over-the-counter treatments can provide temporary relief from symptoms. These include:
- Stool Softeners: These help prevent constipation by softening the stool, making bowel movements less strenuous.
- Topical Creams and Ointments: When applied externally, products containing ingredients such as witch hazel or hydrocortisone can reduce inflammation and provide soothing relief.
- Sitz Baths: Soaking the anal area in warm water for 10 to 15 minutes several times a day can help reduce irritation and promote healing.
These conservative treatments are often very effective in managing mild to moderate symptoms. They can be used as a first-line approach before considering more invasive options.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
When conservative measures are insufficient, minimally invasive procedures may be considered. These techniques aim to reduce the size of internal hemorrhoids or alleviate their symptoms without the need for extensive surgery.
Rubber Band Ligation:
This is a commonly performed procedure for internal hemorrhoids. During the procedure, a small rubber band is placed around the base of the hemorrhoid, cutting off its blood supply. The hemorrhoid eventually shrinks and falls off. Rubber band ligation is typically performed on an outpatient basis. It has a high success rate, though it may require more than one session for optimal results.
Sclerotherapy:
In this procedure, a chemical solution is injected into the hemorrhoidal tissue, shrinking it by inducing fibrosis. Sclerotherapy is less invasive and particularly useful for smaller internal hemorrhoids. It is generally well-tolerated, with minimal discomfort during and after the procedure.
Infrared Coagulation:
This method uses infrared light to coagulate the blood vessels supplying the hemorrhoid, leading to its shrinkage and eventual resolution. Infrared coagulation is another minimally invasive option that is effective for treating internal hemorrhoids, especially in cases where rubber band ligation is not feasible.
Surgical Interventions
Surgery is reserved for severe cases of internal hemorrhoids that do not respond to conservative or minimally invasive treatments. Surgical options are considered when the hemorrhoids are large, prolapsed, or cause significant bleeding and discomfort.
Hemorrhoidectomy:
This is the most definitive surgical treatment for hemorrhoids. It involves the complete removal of the hemorrhoidal tissue. It is usually recommended for large, persistent hemorrhoids that have not responded to other treatments. While hemorrhoidectomy is highly effective, it is associated with a more extended recovery period and may involve significant postoperative pain.
Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy:
Also known as stapled hemorrhoid surgery, this procedure involves repositioning the hemorrhoidal tissue and reducing blood flow using a circular stapling device. Compared to traditional hemorrhoidectomy, stapled hemorrhoidectomy typically results in less postoperative pain and a faster recovery. However, it may not be suitable for all patients, particularly those with extensive disease.
Long-Term Management and Prevention
Even after successful treatment, long-term management of internal hemorrhoids is essential to prevent recurrence. Adopting and maintaining healthy bowel habits can make a significant difference. This includes a consistent high-fiber diet, staying well-hydrated, and engaging in regular physical activity. Avoiding prolonged sitting and minimizing straining during bowel movements are key components of long-term prevention.
Regular follow-up with your healthcare provider is essential, particularly if you have a history of recurring hemorrhoids. They can offer guidance on lifestyle modifications and may recommend periodic examinations to ensure that any new symptoms are addressed promptly.
Psychological and Emotional Considerations
Dealing with internal hemorrhoids, especially when symptoms are chronic or severe, can have an emotional toll. The discomfort, potential embarrassment, and impact on daily activities can contribute to feelings of stress and anxiety. Addressing these psychological aspects as part of a comprehensive treatment plan is essential. Counseling, support groups, or simply discussing your concerns with a trusted healthcare provider can provide reassurance and help you manage the emotional challenges associated with this condition.
Conclusion: Empowering Your Journey to Relief
Internal hemorrhoids are a common yet often manageable condition. With a range of treatment options—from dietary modifications and over-the-counter remedies to minimally invasive procedures and surgery—you have multiple avenues to find relief. Recognizing the symptoms early and adopting proactive strategies can significantly improve your quality of life and reduce the likelihood of complications.
Empower yourself by staying informed about your condition and working closely with your healthcare team to tailor a treatment plan that suits your needs. With effective treatment, preventive measures, and ongoing support, you can manage internal hemorrhoids and take control of your digestive health.
For further information on treatment options and best practices for managing hemorrhoids, you may explore resources available at Mayo Clinic’s Hemorrhoids Overview and the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons.
